Dielectric Polarization and Induced Surface Charges
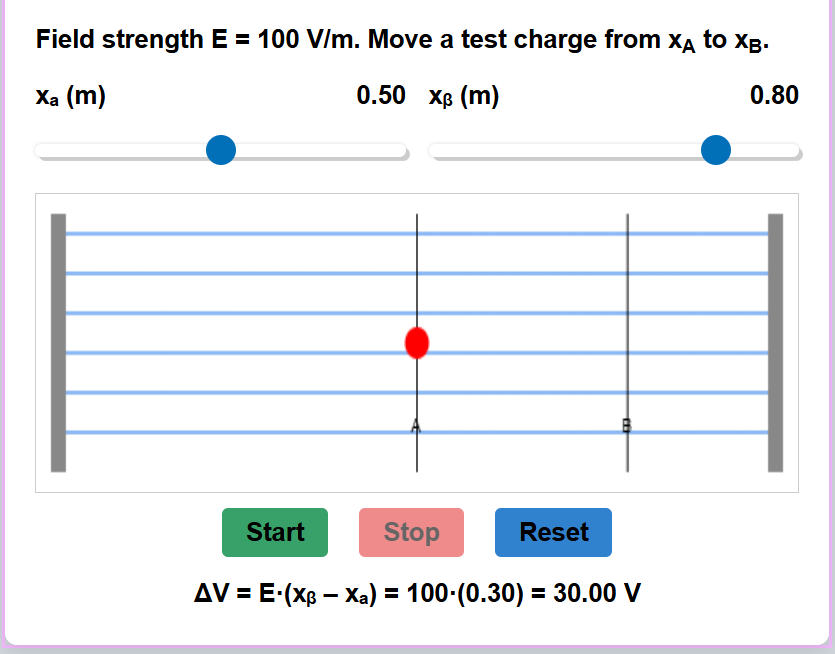
Every volume element Δv of the slab has a dipole moment P Δv in the direction of the field. The volume element Δv is macroscopically small but contains a very large number of molecular dipoles. Anywhere inside the dielectric, the volume element has no net charge (though it has net dipole moment).
At the surfaces of the dielectric normal to the electric field, there is evidently a net charge density. The positive ends of the dipoles remain unneutralized at one surface and the negative ends at the opposite surface. The unbalanced charges are the induced charges due to the external field.
Thus, the polarized dielectric is equivalent to two charged surfaces with induced surface charge densities, say σp and -σp. The field produced by these surface charges opposes the external field.
Dielectric Slab in Electric Field
When no electric field is applied, the dielectric has no net polarization. Turn on the electric field to see the effect.