Capacitors and Capacitance
A capacitor is a system of two conductors separated by an insulator. The conductors have charges Q and -Q, with potential difference V = V1 - V2 between them.
The electric field in the region between the conductors is proportional to the charge Q. The potential difference V is also proportional to Q, and their ratio is constant:
C = Q / V
The constant C is called the capacitance of the capacitor. Capacitance depends only on the geometry of the conductors and the nature of the insulating medium between them.
Parallel Plate Capacitor
Q = 50 µC
d = 10 mm
A = 100 cm²
C = ε₀A/d = 8.85 pF
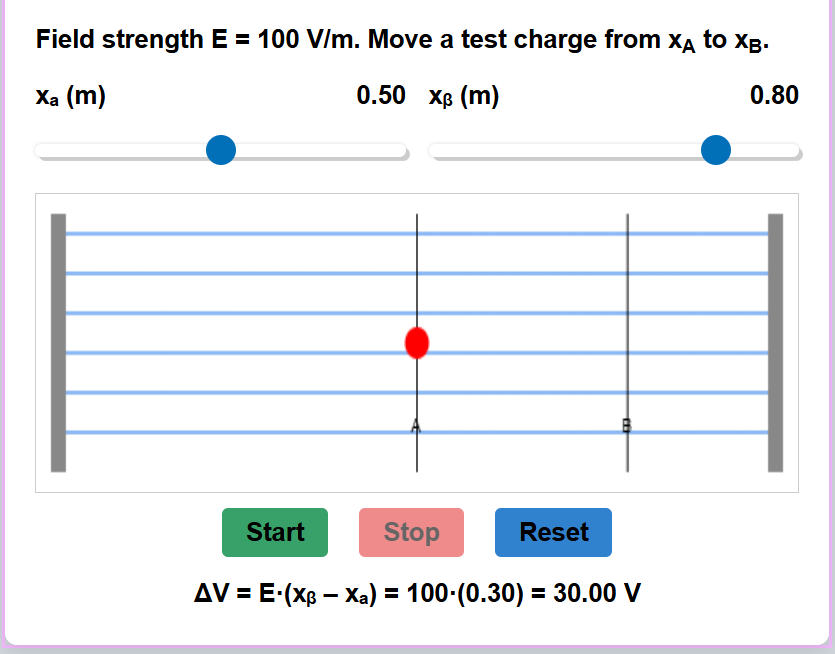
Adjust the sliders to see how charge, plate separation, and plate area affect the capacitance.
The electric field between the plates is proportional to the charge density (Q/A).
Positive Charge
Negative Charge
Electric Field
Conductor
Dielectric